Visualizing the Magic Behind GPT: A Visual Walkthrough for Business Leaders
Understanding the inner workings of large language models, from token embeddings to self-attention, with a simplified visual tool.
Large language models (LLMs) like GPT-3 have become the cornerstone of innovation across industries in artificial intelligence. Their ability to generate text, summarize documents, and even hold conversations transforms how businesses interact with data and customers. However, while the outputs of these models seem almost magical, the underlying mechanics remain a black box for many professionals. That’s where a new visualization tool comes in—designed to shed light on the intricate processes that power these language models.
Source: A work by Brendan Bycroft
This article will explain how large language models work and why understanding their mechanics can benefit business leaders, marketers, and creatives alike.
Demystifying GPT: The Inner Workings of Language Models
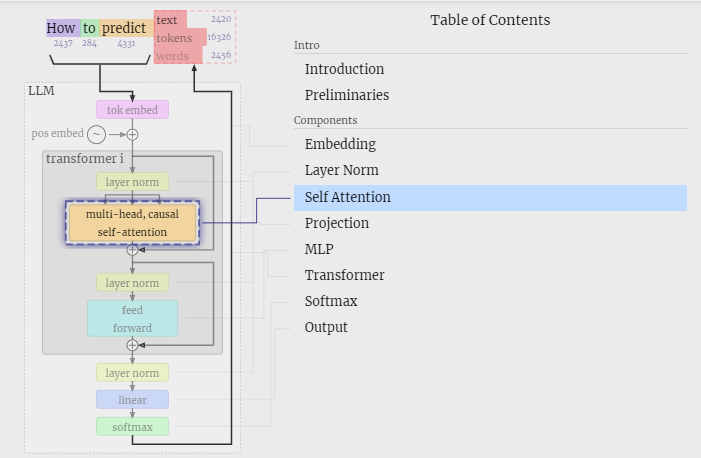
At the heart of LLMs like GPT-3 is a type of neural network architecture known as a transformer, which enables the model to process and generate human-like text. While terms like "self-attention" and "multi-head attention" might sound technical, they are vital components that make these models so powerful. They allow the model to understand the relationship between different words in a sentence—whether those words are next to each other or far apart.
The simplified nano-GPT model, with just 85,000 parameters (compared to the 175 billion in GPT-3), provides a way to see how even a basic transformer can perform tasks like sorting a sequence of letters. In this case, it takes a set of six letters, such as "C B A B B C." It arranges them in alphabetical order, resulting in "A B B B C C." While sorting letters is not the same as writing a blog post or answering customer queries, it highlights how these models manipulate sequences of data, which is fundamental to their success.
Source: A work by Brendan Bycroft
Key Components Explained
The visualization tool breaks down the model into several components:
Embedding: Before the model can process words (or, in this case, letters), it needs to convert them into numerical values through embeddings. These embeddings capture each token's "meaning" or context, allowing the model to understand them.
Positional Embedding: Unlike traditional neural networks that process data sequentially, transformers don’t have an inherent sense of order. Positional embeddings allow the model to know where each token appears in the sequence.
Self-Attention Mechanism: The most powerful aspect of the transformer architecture, self-attention allows the model to focus on essential relationships between tokens. For example, in the sentence "The cat sat on the mat," the model might pay special attention to the relationship between "cat" and "sat" while ignoring less relevant words like "the."
Layer Normalization: A technique to stabilize and improve the training process by ensuring that inputs to each model layer are well-behaved (i.e., normalized).
Feed-Forward Neural Network: This part of the model processes the outputs from the self-attention mechanism and converts them into valuable predictions.
Softmax: The final layer that produces the model’s output—in this case, arranging the letters in the correct order.
Source: A work by Brendan Bycroft
Why Is This Relevant to Business?
While understanding the technical aspects of LLMs may not seem necessary for business leaders, gaining a basic understanding of how these models function can lead to better decision-making when deploying AI-driven solutions. Here's why:
Data-Driven Decisions: For businesses that rely on large volumes of data—whether in marketing, customer support, or operations—understanding how GPT models process language can lead to more effective use of AI. Leaders can better assess which tasks are best suited for automation and where human oversight is necessary.
Enhancing Creativity: LLMs open the door to unprecedented levels of creative support for marketers and creative professionals. Whether generating copy, brainstorming ideas, or refining messages, GPT models can be a powerful tool when used correctly. Knowing how these models work can help creative teams explore new ways to collaborate with AI.
Trust in AI: One of the most significant barriers to widespread AI adoption is trust. By making the workings of these models more transparent, businesses can build greater confidence in AI tools. A clearer understanding of how models like GPT-3 generate text can lead to greater acceptance and more ethical use of AI in areas like content creation and customer engagement.
Industry Use Cases
E-commerce: Thanks to LLMs, personalized product recommendations are becoming more precise. By understanding user behaviour and preferences through text data (reviews, searches, etc.), models like GPT can generate personalized suggestions, increasing conversion rates.
Healthcare: In the medical field, LLMs are being used to assist doctors by summarizing patient records, analyzing symptoms, and even generating initial diagnoses. Understanding how these models work can help healthcare providers trust these systems in life-critical situations.
Customer Service: Companies increasingly use chatbots and automated response systems powered by LLMs. Understanding the model’s limitations—such as its dependence on training data—can help businesses design better customer experiences and avoid common pitfalls like irrelevant or inappropriate responses.
A Peek into the Future
As AI continues to evolve, visual tools like this one are helping to make LLMs more accessible to data scientists and the broader business community. By breaking down the "black box" and providing insight into how these models function, professionals across industries can make smarter, more informed decisions about incorporating AI into their strategies.
Whether you're a CEO looking to streamline operations, a marketer seeking new creative avenues, or a developer exploring AI’s capabilities, understanding the foundational mechanics of models like GPT is no longer optional—it’s essential for staying competitive in the rapidly changing digital landscape.