How Generative AI is Fueling a Data Center Boom
Massive Investments, Cooling Challenges, and New Markets in the Race to Power AI
The Rise of AI-Driven Data Centers
Generative AI has ignited an unprecedented expansion in data center investments, transforming traditional infrastructures to support the rapid scaling of machine learning models, natural language processing, and image generation. This year alone, major players like Amazon, Microsoft, Google, and Meta invested over $52 billion in data centers, a nearly 60% increase year-over-year. As demand for AI accelerates, so too does the need for faster, more powerful, and energy-efficient data centers, creating both challenges and opportunities across the industry.
Andy Jassy, CEO of Amazon, encapsulated the trend during a recent earnings call: "The faster we grow demand, the faster we have to invest capital in data centers and networking gear and hardware.” In Q3 2024, Amazon invested a staggering $22.6 billion in capital expenditures (82% of AWS’s revenue) primarily to support AI infrastructure. Similar investments across big tech reflect the urgency with which these companies are racing to meet escalating demands for AI workloads.
Source: CB Insights, 2024
Why Generative AI is Straining Data Centers
Data centers have always been the backbone of digital operations, but generative AI has fundamentally reshaped the demands placed on them. Traditional computing requires data centers that store, retrieve, and process data at moderate speeds and with limited complexity. In contrast, AI workloads involve processing vast datasets through complex machine learning models that need high computational power, specialized hardware, and continuous learning cycles. Here’s why these demands are fundamentally different:
High Compute Intensity: Generative AI models, like GPT-4 or DALL-E, run on large-scale neural networks with billions (or even trillions) of parameters. This requires a massive amount of processing power, necessitating GPUs and, increasingly, specialized AI accelerators like TPUs.
Data Storage and Access: Unlike traditional applications, AI applications require substantial amounts of fast-access data storage, especially during model training and retraining.
Energy Demands: Data centers handling AI workloads often consume up to 4-5 times the energy required by conventional data centers, straining both power grids and budgets.
Cooling Challenges: With the immense heat generated by AI operations, advanced cooling solutions are essential to maintain system stability, sparking innovations in liquid cooling, immersion cooling, and heat reusability.
Why It’s Relevant Now
The rapid expansion of generative AI is compelling tech giants to make aggressive investments in data centers. This is more than just a technological shift; it's reshaping capital expenditure strategies for the world’s biggest companies, making AI infrastructure one of the most significant capital-intensive areas in tech today. Data centers aren’t just growing in number—they’re evolving to be more energy-efficient and resilient, particularly as companies explore green energy sources like nuclear power to manage the costs and environmental impacts of their AI operations.
These AI-centered data centers are also a driving force in new markets. The data center supply chain is diversifying to include high-performance computing hardware, sustainable energy solutions, and advanced cooling infrastructure. As companies scale their AI capabilities, these tech markets—each with high growth potential—are seeing a spike in demand, creating fresh opportunities for innovation.
What’s at Stake for Business Leaders
For C-suite executives, the rise of AI-powered data centers is a signal that cloud providers, data infrastructure providers, and even energy suppliers are becoming critical partners in maintaining AI competitiveness. Here’s how this trend is impacting key areas:
Cost Allocation: With the growing necessity to allocate substantial funds to AI data infrastructure, businesses must consider long-term investment in cloud resources and partnerships with data center providers to remain competitive.
Operational Efficiency: As data centers consume more power and produce more heat, leaders face a strategic question: how to manage operational costs while delivering on AI’s potential? The choice of data centers, energy sources, and cooling methods could make or break the business case for enterprise AI.
Sustainability Goals: Many businesses have set ambitious sustainability targets. Given the energy intensity of AI, they’ll need to align with data center providers focused on renewable or low-emission energy sources.
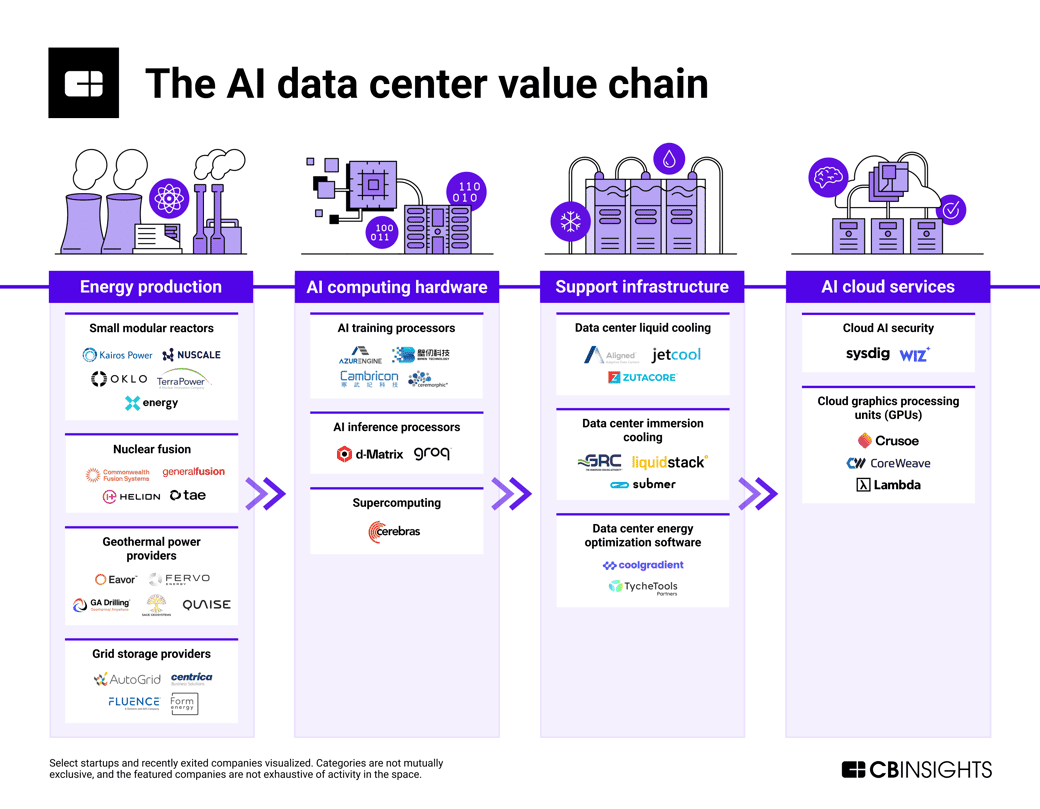
High-Momentum Markets in the AI Data Center Value Chain
With AI reshaping the data center landscape, multiple markets within this ecosystem are poised for growth. Here’s a look at the tech markets that are surging as data centers evolve to support generative AI:
Advanced AI Hardware: This includes GPUs, TPUs, and emerging AI accelerators that are optimized for handling the high-intensity computations required by generative AI.
Liquid and Immersion Cooling: Cooling solutions are becoming critical, especially in energy-efficient configurations that lower operational costs. Technologies like immersion cooling can help manage the heat produced by dense AI workloads, offering a scalable solution as demands rise.
Green Energy Solutions: Many data centers are exploring green energy sources to power their operations. Partnerships with nuclear, solar, and wind energy providers are increasingly common.
Data Storage Technologies: AI relies on accessible, high-capacity storage solutions, making storage providers another key player in the data center ecosystem.
Edge Computing: As data generation grows, edge computing allows processing closer to the data source, which reduces latency for real-time AI applications, such as in autonomous vehicles or smart cities.
Networking Infrastructure: High-bandwidth networking solutions are essential for moving data at the speeds required by AI, paving the way for increased investments in fiber optics, 5G, and beyond.
Case Studies in Industry
Energy Sector: Renewable energy providers are partnering with tech giants to provide sustainable power solutions tailored for AI-heavy data centers. These partnerships are helping companies like Google and Microsoft reach their ambitious zero-carbon goals.
Automotive: With the rise of autonomous driving, automotive companies are investing in edge data centers near production hubs to support low-latency data processing, ensuring real-time responsiveness in safety-critical systems.
Healthcare: AI-driven diagnostics and drug discovery require massive computing power, prompting collaborations with cloud providers that offer AI-optimized data centers to support this level of data-intensive research.
The Future of Data Centers in an AI-Driven World
As generative AI continues to expand, data centers are poised to be at the center of a profound shift in enterprise infrastructure. This growth will extend far beyond the tech giants, shaping strategies across industries that are integrating AI into their products and services. With innovations in cooling, energy, and specialized hardware, the data center landscape will evolve toward efficiency and sustainability, bridging the needs of high-performance AI with environmental responsibility.
For companies considering investments in AI, the data center is no longer a secondary concern but a primary enabler of generative AI capabilities. The race is on—and for businesses ready to adapt, the rewards promise to be as transformative as AI itself.